信息整理:图书馆
2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖授予美国科学家玛丽・E・布伦科(Mary E. Brunkow)、弗雷德・拉姆斯德尔(Fred Ramsdell)和日本科学家坂口志文(Shimon Sakaguchi),以表彰他们“在外周免疫耐受方面的发现”。以下对三位获奖者的相关主题学术论文及其施引文献展开分析。
一、获奖者发文分析
2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获奖者Mary E. Brunkow、Fred Ramsdell和Shimon Sakaguchi“在外周免疫耐受方面的发现”所发表的SCIE论文230篇(文献类型限制为Article/Review),发文的年度分布如图1所示。
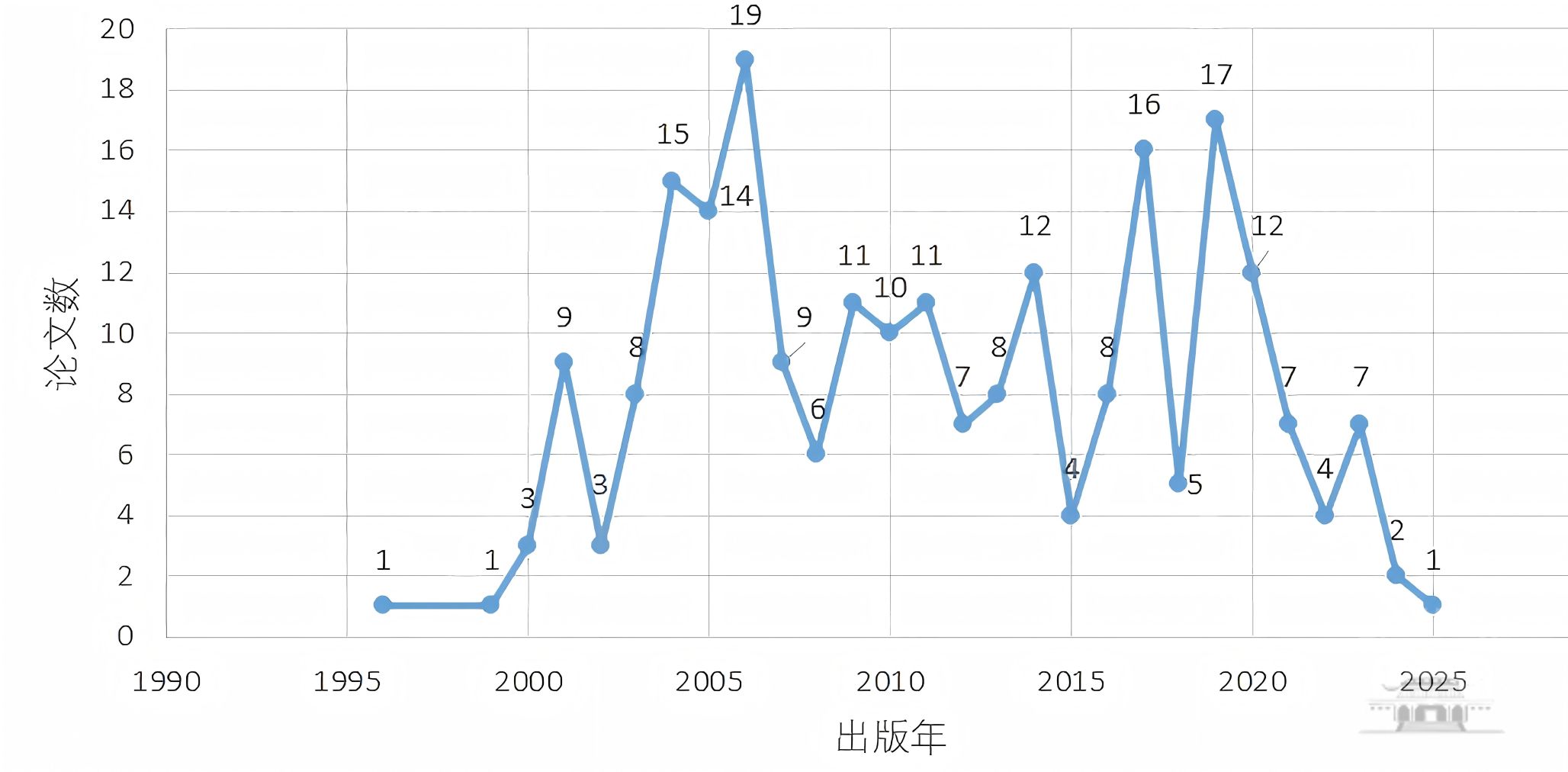
图1 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获奖者相关主题SCIE论文年度分布
相关主题论文230篇发表在92种期刊上,其中,2篇发表在Cell上,2篇发表在Nature上,3篇发表在Science上。
通过对230篇相关主题论文的关键词进行词频统计,得到的高频关键词词云如图2,主要高频词有:regulatory T cells (95)、immunological self-tolerance(56)、Foxp3 (55)、expression (43)、induction (42)、dendritic cells (35)、autoimmune-disease (31)等。

图2 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获奖者相关主题论文的高频关键词词云图
二、相关施引文献分析
截至2025年10月15日,三位获奖者的230篇诺奖相关主题论文被全球42,173篇论文引用,总被引75,929次,篇均被引330.13次。从全球来看,施引文献呈逐年持续增长趋势,2021年高达2866篇,近几年略有回落,发文年度分布见图3。
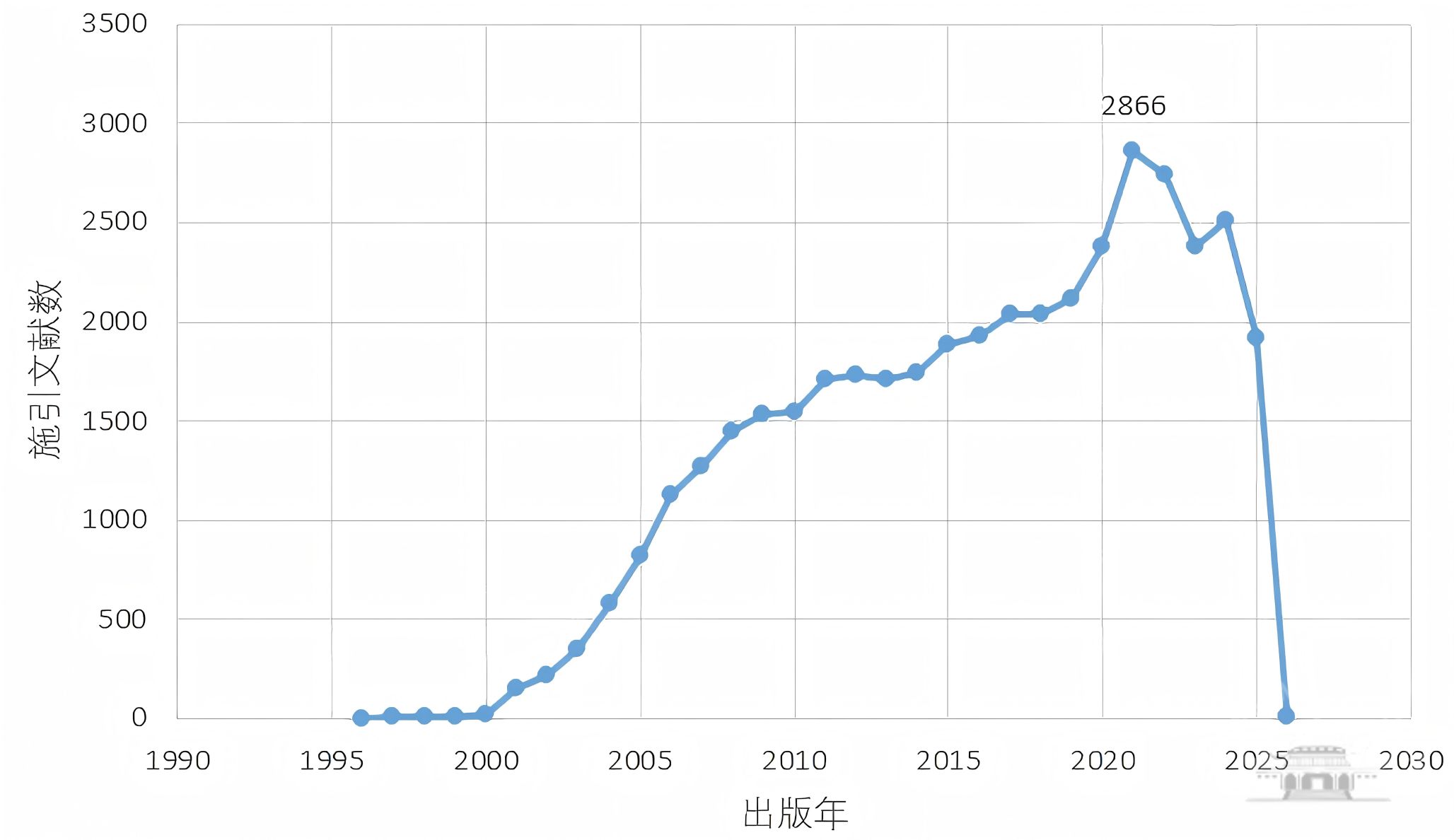
图3 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献年度分布
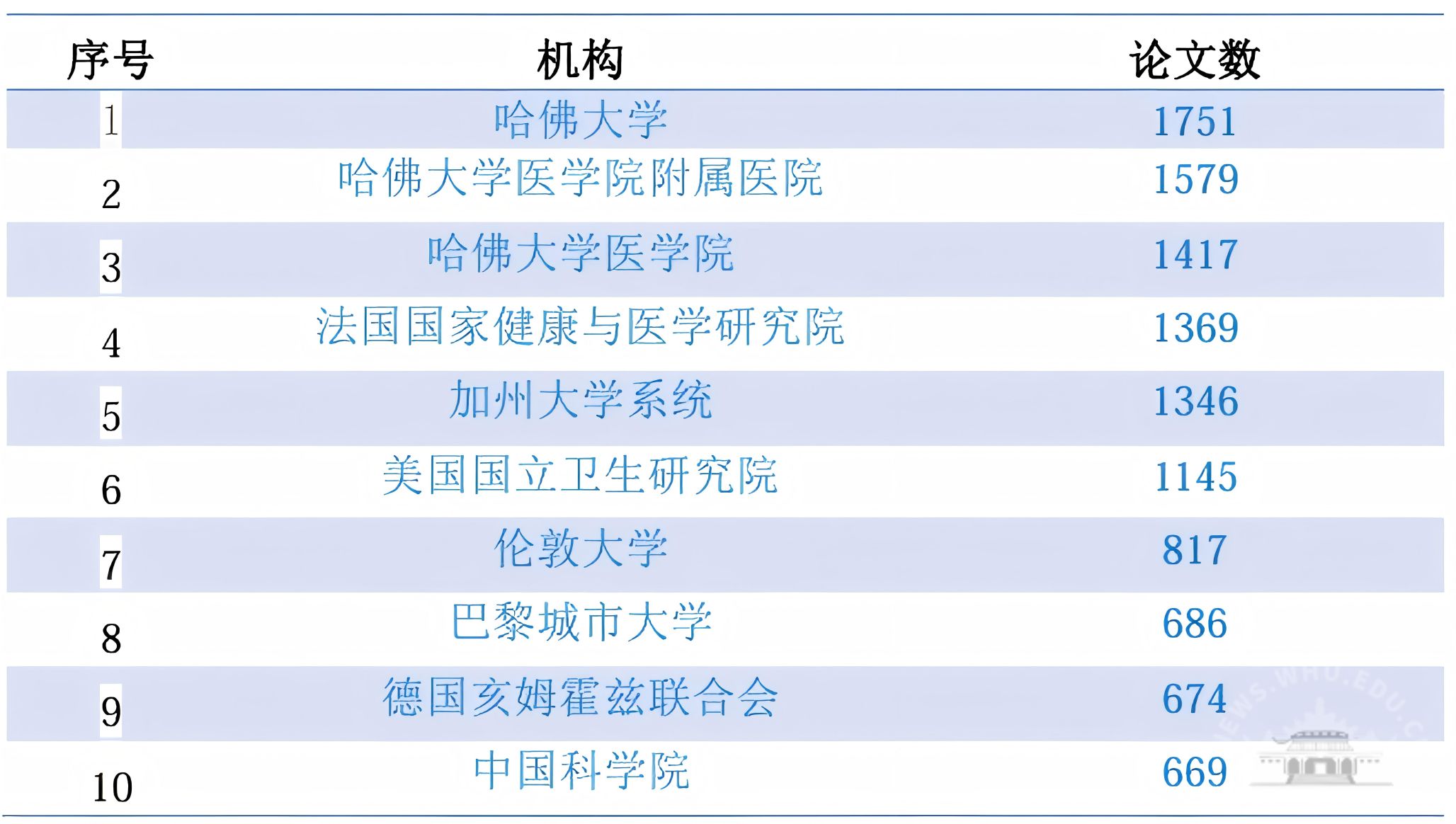
全部施引文献分布在146个国家/地区;论文数排名第一的是美国,随后是中国、日本。发文量前十的国家/地区见表1;表2列出了发文量前十的机构。
表1 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献中发文量TOP 10的国家/地区
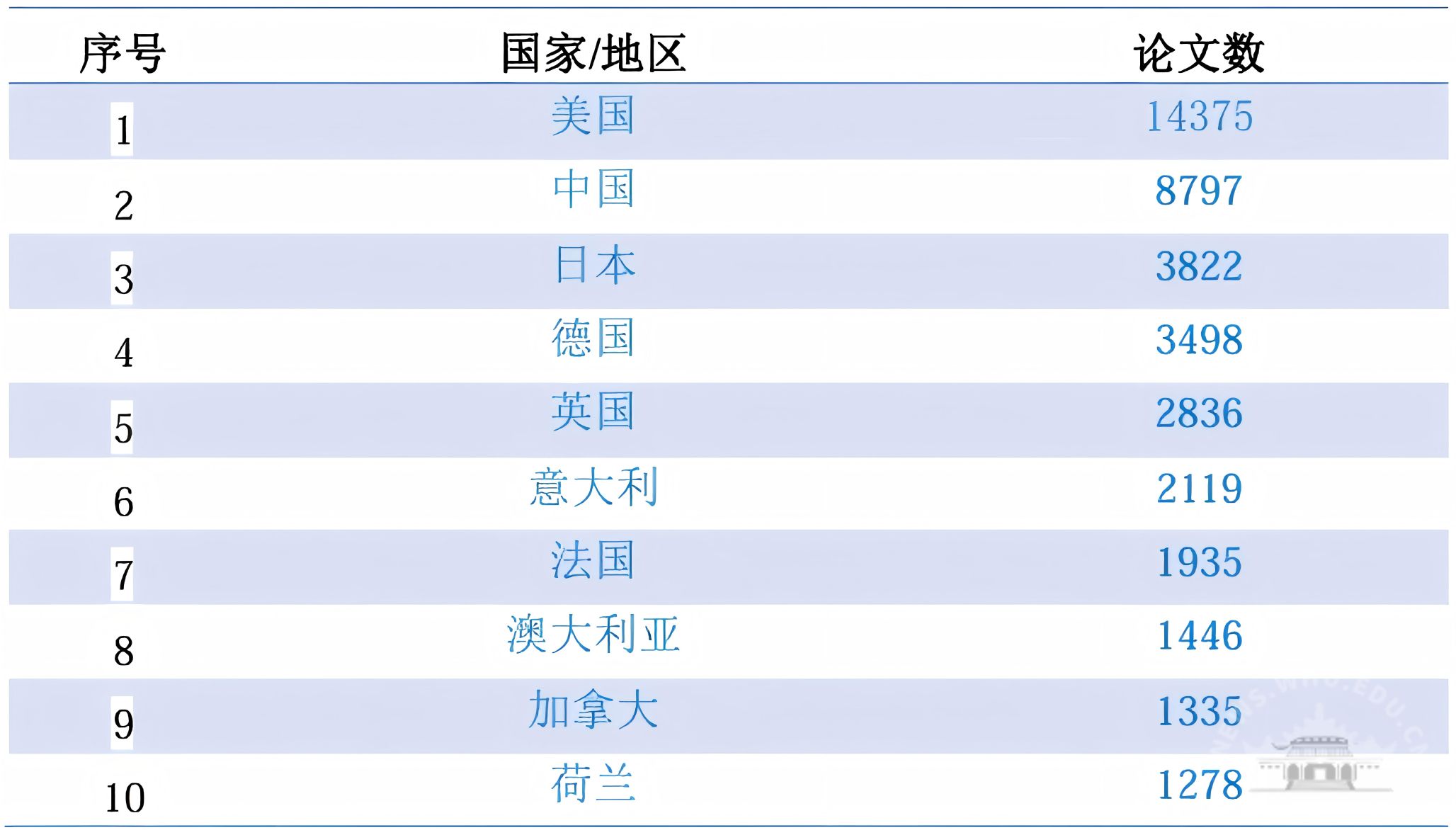
表2 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献中发文量TOP 10的机构
中国作者参与的共有8797篇文献引用了三位诺贝尔奖获奖者相关主题论文,发文年度分布见图4,论文逐年持续增长,2024年达到峰值(1124篇)。
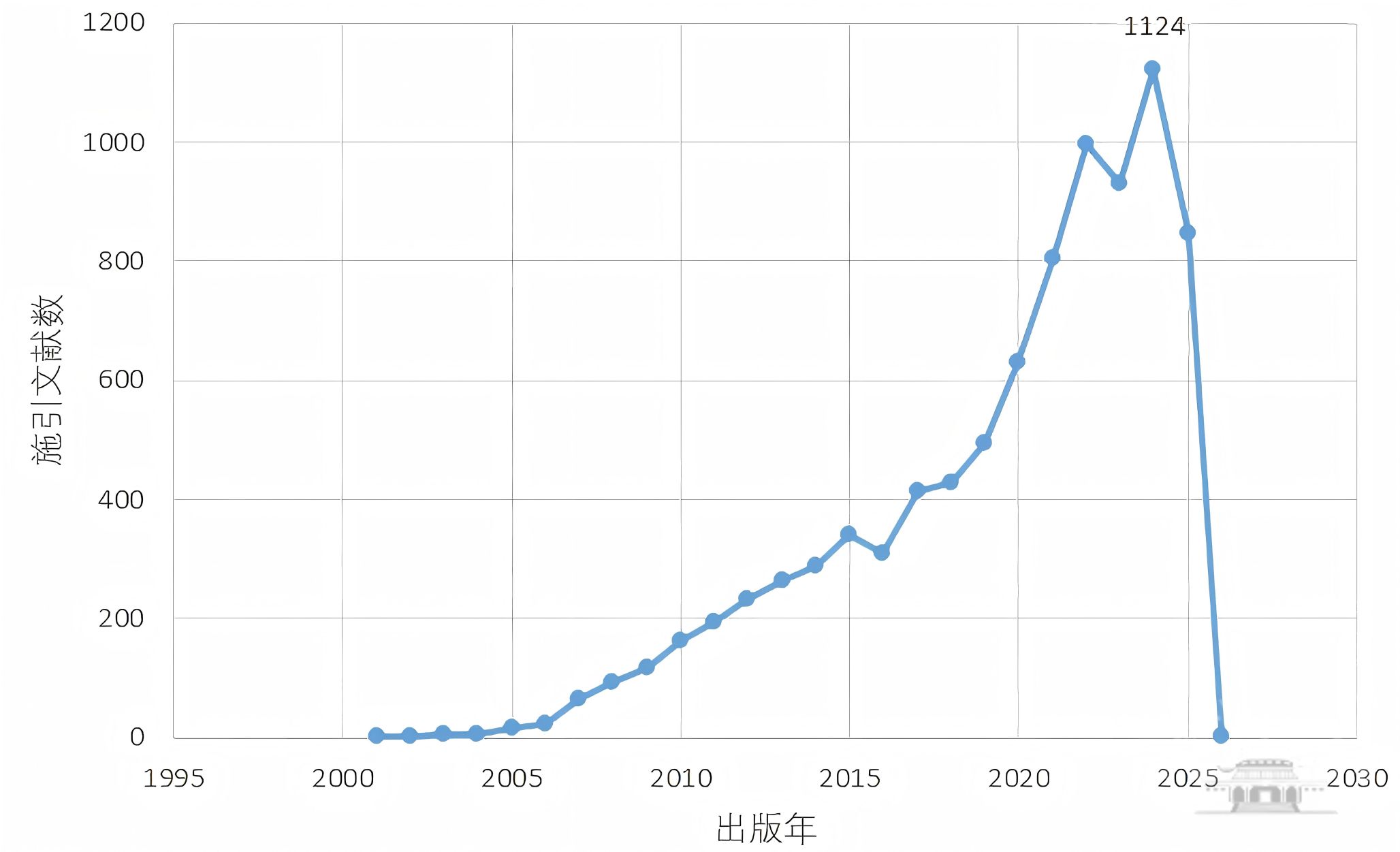
图4 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖中国作者参与的相关施引文献年度分布
中国作者参与的8797篇论文分布在1532种期刊上,发文较多的 20 种期刊刊载相关论文2083篇,占8797篇的23.68%。TOP 20期刊见图5。
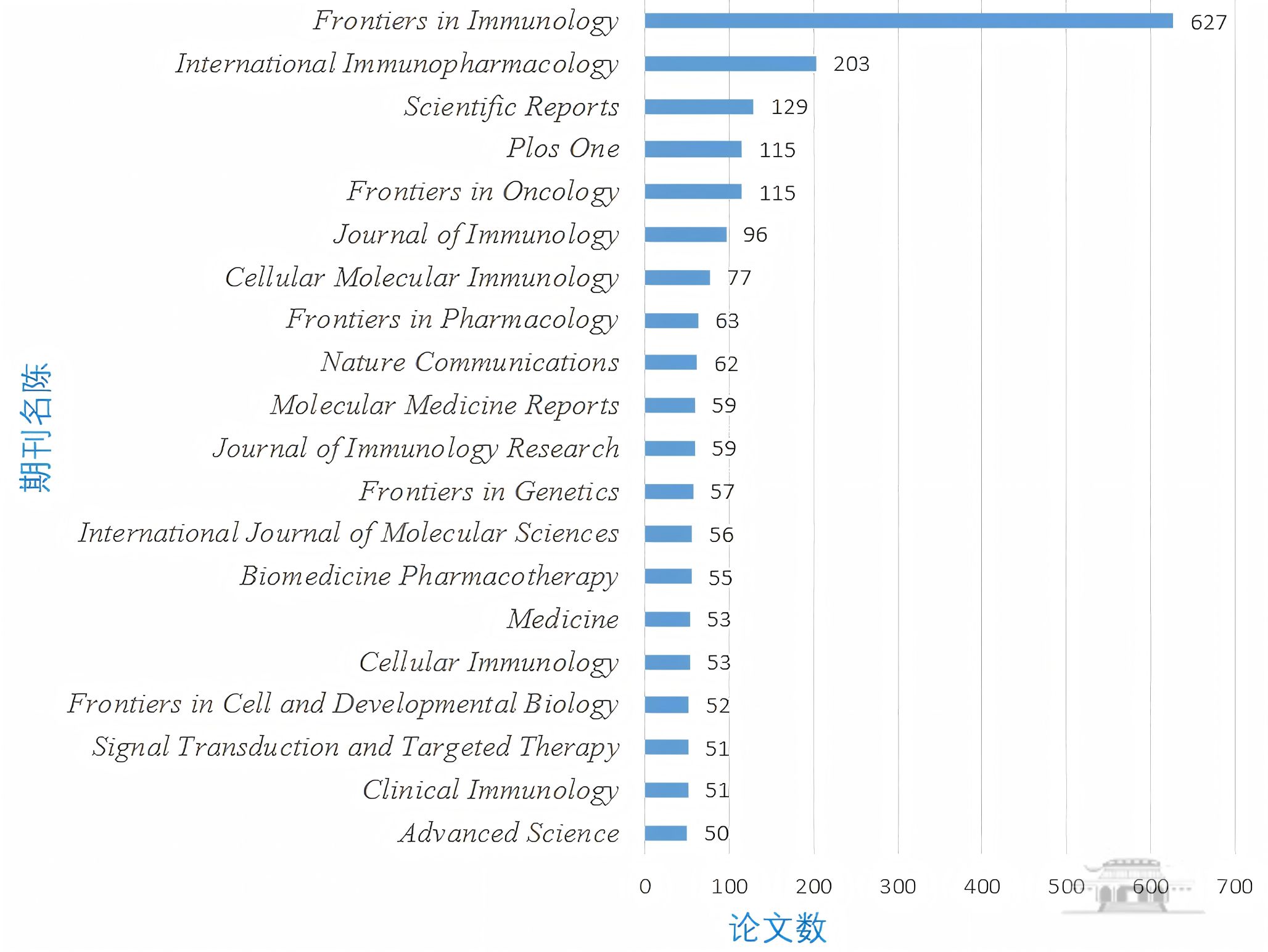
图5 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖中国作者参与的相关施引文献期刊分布(TOP 20)
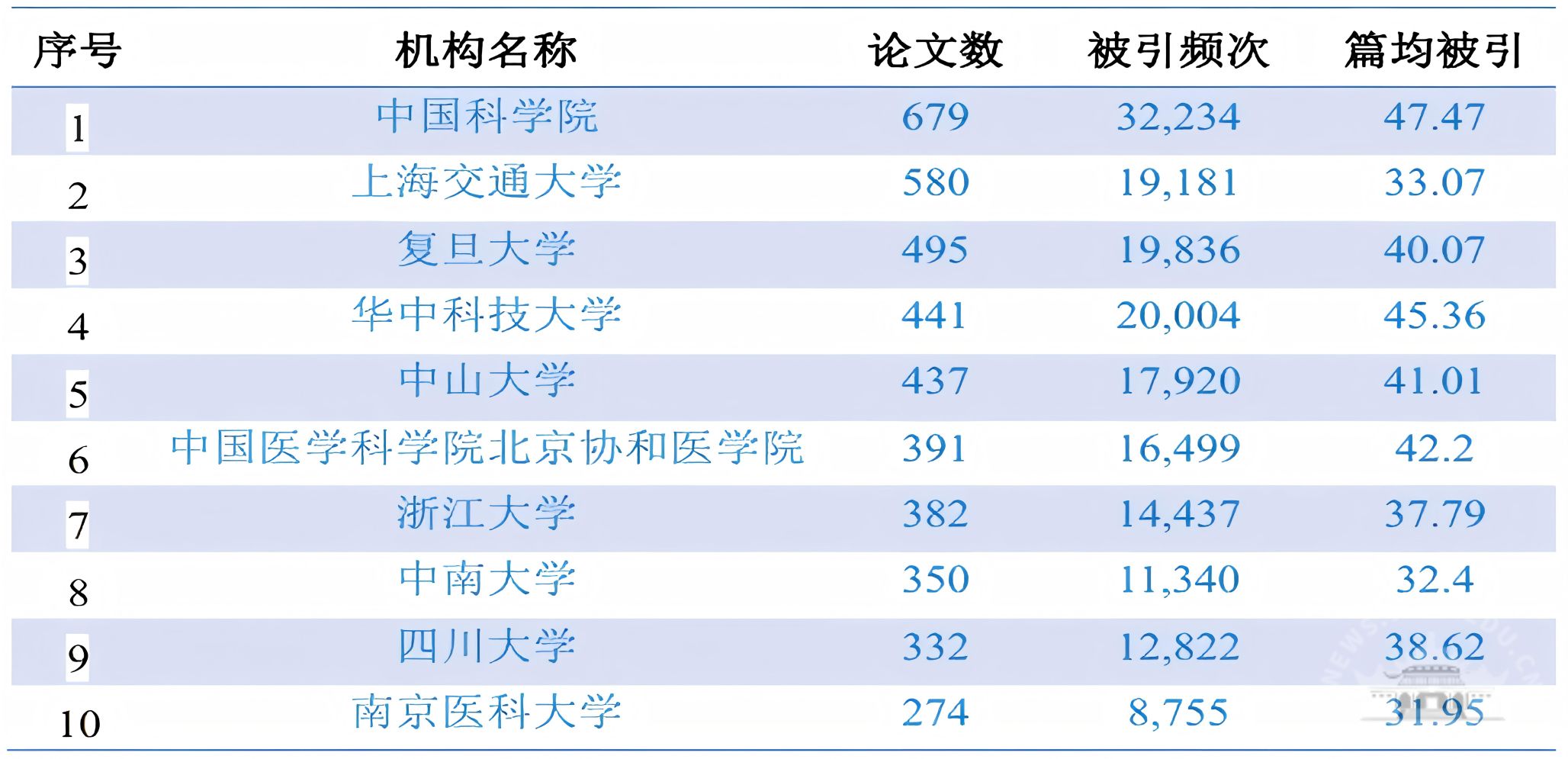
8797篇相关施引文献中发文量>100篇的中国机构有45家,排名前十的中国机构及其相应成果表现详见表3。
表3 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献中发文量TOP 10的中国机构
使用VOSviewer对中国作者参与的8797篇施引文献的关键词进行共现分析(设置阈值为40),形成的关键词共现图,见图6,其中节点代表关键词,节点的大小表示该关键词的出现频率,节点之间的连线表示关键词之间的共现关系。
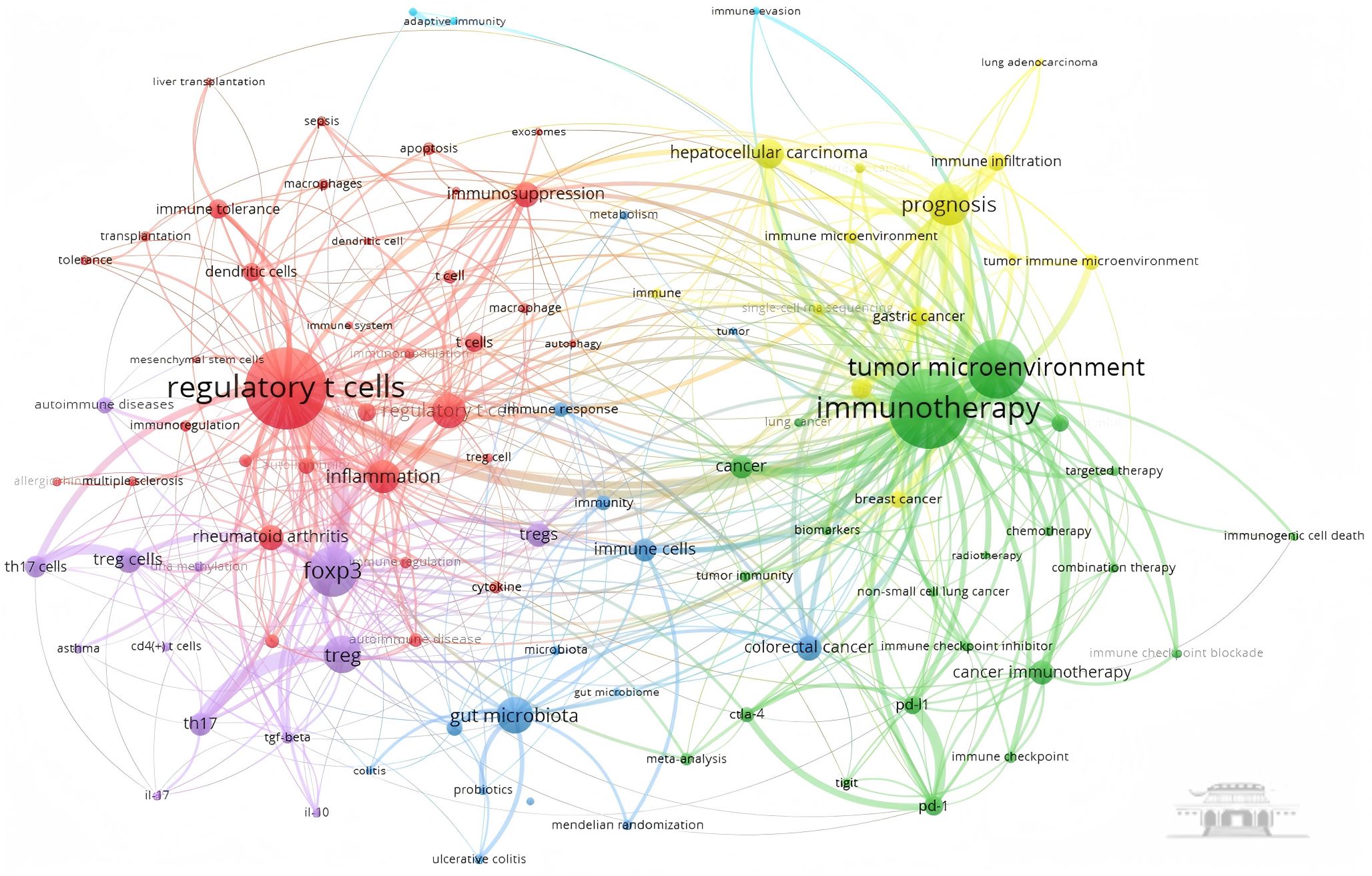
图6 2025年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖中国作者参与的相关施引文献关键词共现图
三、获奖者相关主题高被引论文
三位获奖者的230篇诺奖相关主题文献中有高被引论文10篇,列举如下(ESI更新时间:2025年9月),供参考。
[1]Tay C, Tanaka A, Sakaguchi S.Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells as targets of cancer immunotherapygulatory T cells as targets of cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancer Cell. 2023, 41(3): 450-465.
[2] Cossarizza A, Chang H D, Radbruch A, et al.Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (third edition)[J]. European Journal of Immunology. 2021, 51(12): 2708-3145.
[3] Tekguc M, Wing J B, Osaki M, et al.Treg-expressed CTLA-4 depletesCD80/CD86by trogocytosis, releasing free PD-L1 on antigen-presentingcells[J/OL].Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of TheUnited States of America. 2021, 118(30) (2021-07-27)[2025-10-20.].https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.202373911.
[4] Sakaguchi S, Mikami N, Wing J B, et al.Regulatory T Cells and Human Disease[Z]. Annual Review of Immunology 2020: 38, 541-566.
[5] Tanaka A, Sakaguchi S.Targeting Treg cells in cancer immunotherapy[J]. European Journal of Immunology. 2019, 49(8): 1140-1146.
[6] Kamada T, Togashi Y, Tay C, et al.PD-1+ regulatory T cells amplified by PD-1 blockade promote hyperprogression of cancer[J]. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America. 2019, 116(20): 9999-10008.
[7] Wing J B, Tanaka A, Sakaguchi S.Human FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cell Heterogeneity and Function in Autoimmunity and Cancer[J]. Immunity. 2019, 50(2): 302-316.
[8] Tanaka A, Sakaguchi S.Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cell Research. 2017, 27(1): 109-118.
[9] Saito T, Nishikawa H, Wada H, et al.Two FOXP3+CD4+ T cell subpopulations distinctly control the prognosis of colorectal cancers[J]. Nature Medicine. 2016, 22(6): 679-+.
[10] Ohnmacht C, Park J H, Cording S, et al.The microbiota regulates type 2 immunity through RORγt+ T cells[J]. Science. 2015, 349(6251): 989-993.
四、高影响力施引文献
施引文献中高被引论文857篇、热点论文18篇(ESI更新时间:2025年9月),下面列举18篇热点论文信息供参考。
[1]Neurath M F, Artis D, Becker C.The intestinal barrier: a pivotal role in health, inflammation, and cancer[J]. Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2025, 10(6): 573-592.
[2] Slominski R M, Chander R, Jetten A M, et al.Neuro-immuno-endocrinology of the skin: how environment regulates body homeostasis[J]. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2025, 21(8): 495-509.
[3]The interplay between gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and implications for host health and disease[J/OL]. Gut Microbes. 2024, 16(1) (2024-12-31) [2025-10-22].https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2024.2393270.
[4] Hossain M A.A comprehensive review of immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer treatment[J/OL]. International Immunopharmacology. 2024, 143. (2024-12-25) [2025-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113365.
[5] Wu B, Zhang B, Li B W, et al.Cold and hot tumors: from molecular mechanisms to targeted therapy[J/OL]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2024, 9(1). (2024-10-18) [2025-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01979-x.
[6] Redenti A, Im J, Redenti B, et al.Probiotic neoantigen delivery vectors for precision cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature. 2024, 635:453–461.
[7] Li Q, Geng S, Luo H, et al.Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer: pathogenesis and targeted therapy[J/OL]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2024, 9(1). (2024-10-07) [2025-10-22].https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01953-7.
[8] Liu J Y, Bai Y N, Li Y G, et al.Reprogramming the immunosuppressivetumor microenvironment through nanomedicine: an immunometabolismperspective[J/OL]. Ebiomedicine. 2024, 107. (2024-8-22) [2025-10-22] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105301.
[9] Berndt C, Alborzinia H, Amen V S, et al.Ferroptosis in health and disease[J/OL]. Redox Biology. 2024, 75. (2024-9) [2025-10-22].https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103211.
[10] Lin X, Kang K, Chen P, et al.Regulatory mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancers[J/OL]. Molecular Cancer. 2024, 23(1).(2024-5-18) [2025-10-23]. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-024-02023-w.
[11] Paul S, Konig M F, Pardoll D M, et al.Cancer therapy with antibodies[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2024, 24(6): 399-426.
[12] Neurath M F.Strategies for targeting cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2024, 24(8): 559-576.
[13] Loh J S, Mak W Q, Tan L, et al.Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases[J/OL]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2024, 9(1).(2024-2-16) [2025-10-23]https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01743-1.
[14] Heras-Murillo I, Adán-Barrientos I, Galán M, et al.Dendritic cells as orchestrators of anticancer immunity and immunotherapy[J]. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology. 2024, 21(4): 257-277.
[15] Kumar M A, Baba S K, Sadida H Q, et al.Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases[J/OL]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2024, 9(1). (2024-2-05) [2025-10-23]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01735-1.
[16] Tan Y H, Wang Z H, Xu M T, et al.Oral squamous cell carcinomas: state of the field and emerging directions[J/OL]. International Journal of Oral Science. 2023, 15(1). (2023-9-22) [2025-10-23]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-023-00249-w.
[17] Rui R, Zhou L Q, He S M.Cancer immunotherapies: advances and bottlenecks[J/OL]. Frontiers in Immunology. 2023, 14. (2023-8-24) [2025-10-23].https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1212476.
[18] Di Vincenzo F, Del Gaudio A, Petito V, et al.Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: a narrative review[J]. Internal and Emergency Medicine. 2024, 19(2): 275-293.
(编辑:张惠荣 审核:刘颖、邵敏)