信息整理:图书馆
2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖授予维克托·安布罗斯(Victor Ambros)和加里·鲁夫昆(Gary Ruvkun),以表彰他们发现微小核糖核酸(microRNA)及其在转录后基因调控中的作用。以下对两位获奖者的相关主题学术论文及相关施引文献展开分析。
一、 获奖者发文分析
2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获奖者Victor Ambros和Gary Ruvkun在发现微小核糖核酸(microRNA)及其在转录后基因调控中的作用方面的SCIE论文99篇(文献类型限制为Article),发文的年度分布如图1所示。
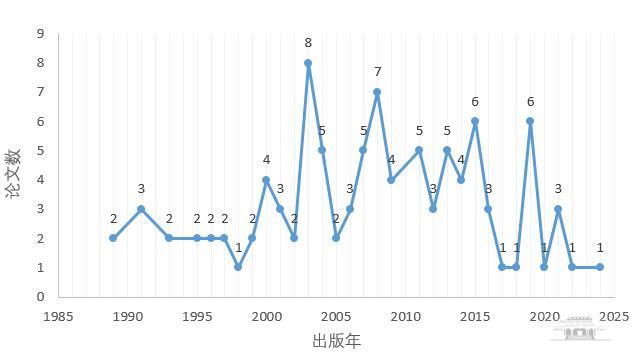
图1 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获奖者相关主题SCIE论文年度分布
相关主题论文99篇发表在33种期刊上,其中,10篇发表在Cell上,5篇发表在Nature上,3篇发表在Science上。
通过对99篇相关主题论文的关键词进行词频统计,得到的高频关键词词云如图2,主要高频词有:C-elegans(81)、microRNA(40)、expression(34)、gene(27)、identification(19)、protein(17)、let-7(16)等。
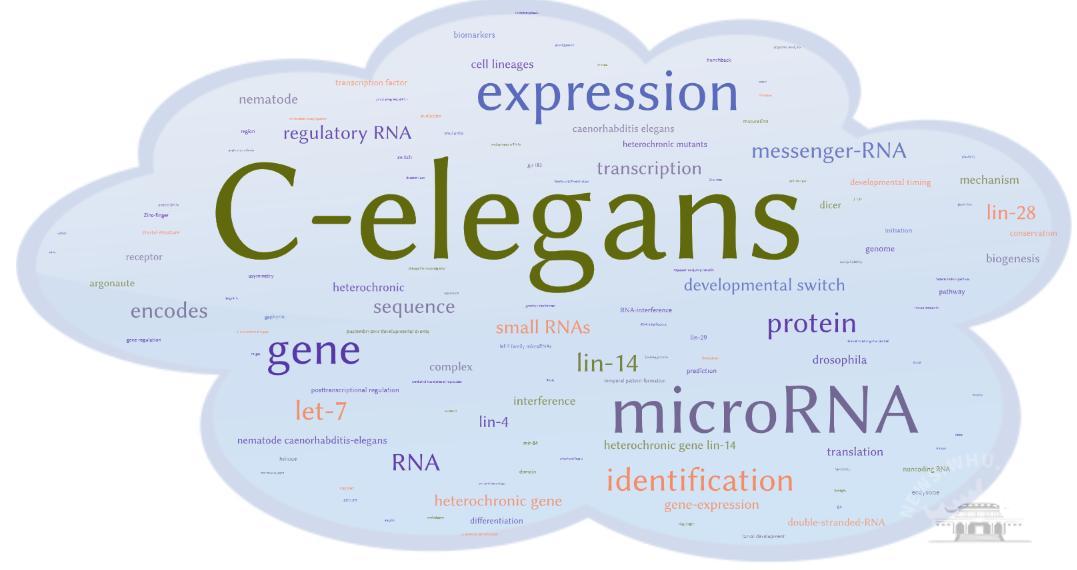
图2 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关主题论文的高频关键词词云
二、 相关施引文献分析
截至2024年10月22日,Victor Ambros和Gary Ruvkun的99篇诺奖相关主题论文被全球29732篇论文引用,总被引48785次,篇均被引492.78次。从全球来看,施引文献逐年持续增长,2015年高达1906篇,发文年度分布见图3。

图3 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献年度分布
全部施引文献分布在122个国家/地区;论文数排名第一的是中国,随后是美国、德国。发文量前十的国家/地区见表1;表2列出了发文量前十的机构,从表2可见中国有三家机构位居前十行列,分别是中国科学院、南京医科大学、上海交通大学。
表1 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献中发文量TOP 10的国家/地区
序号 |
国家/地区 |
论文数 |
1 |
中国 |
9975 |
2 |
美国 |
8763 |
3 |
德国 |
1490 |
4 |
日本 |
1100 |
5 |
英国 |
1064 |
6 |
意大利 |
1043 |
7 |
加拿大 |
865 |
8 |
印度 |
807 |
9 |
澳大利亚 |
701 |
10 |
法国 |
698 |
表2 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献中发文量TOP 10的机构
序号 |
机构 |
论文数 |
1 |
加利福尼亚大学系统 |
874 |
2 |
哈佛大学 |
769 |
3 |
中国科学院 |
708 |
4 |
哈佛医学院 |
555 |
5 |
德克萨斯大学系统 |
533 |
6 |
霍华德·休斯医学研究所 |
503 |
7 |
南京医科大学 |
444 |
8 |
俄亥俄大学系统 |
430 |
9 |
上海交通大学 |
419 |
10 |
美国国立卫生研究院 |
392 |
中国作者参与的共有9975篇文献引用了两位诺贝尔奖获得者相关成果,发文年度分布见图4,论文逐年持续增长,2019年达到峰值(934篇),增长趋势与全球基本一致。
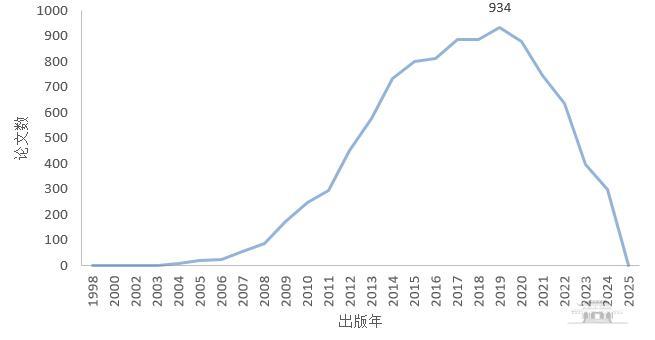
图4 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖中国作者参与的相关施引文献年度分布
9975篇论文分布在1602种期刊上,发文较多的 20 种期刊刊登相关论文2607篇,占全9975的26.14%。TOP 20期刊见图5。
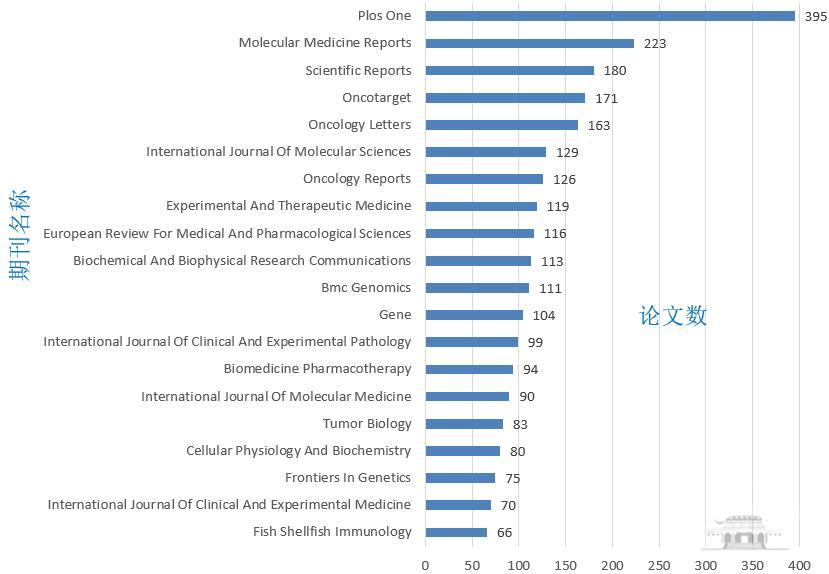
图5 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖中国作者参与的相关施引文献期刊分布(TOP 20)
9975篇相关施引文献中发文量大于100篇的中国机构有41家,排名前十的中国机构及其成果表现详见表3。
表3 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖相关施引文献中发文量TOP 10的中国机构
序号 |
机构名称 |
论文数 |
被引频次 |
篇均被引 |
学科规范化的引文影响力 |
1 |
中国科学院 |
708 |
44340 |
62.63 |
2.09 |
2 |
南京医科大学 |
444 |
21008 |
47.31 |
1.82 |
3 |
上海交通大学 |
419 |
22594 |
53.92 |
1.94 |
4 |
中山大学 |
368 |
22688 |
61.65 |
2.07 |
5 |
浙江大学 |
329 |
13281 |
40.37 |
1.57 |
6 |
中南大学 |
321 |
12388 |
38.59 |
1.60 |
7 |
复旦大学 |
302 |
13650 |
45.19 |
1.73 |
8 |
农业农村部 |
293 |
6881 |
23.48 |
0.99 |
9 |
中国科学院大学 |
229 |
9874 |
43.11 |
1.73 |
10 |
南京大学 |
223 |
14216 |
63.75 |
2.00 |
使用VOSviewer对中国作者参与的9975篇施引文献的关键词进行共现分析,见图6。图谱中节点代表关键词,节点的大小表示该关键词的出现频率,节点之间的连线表示关键词之间的共现关系,相同颜色代表一个聚类。
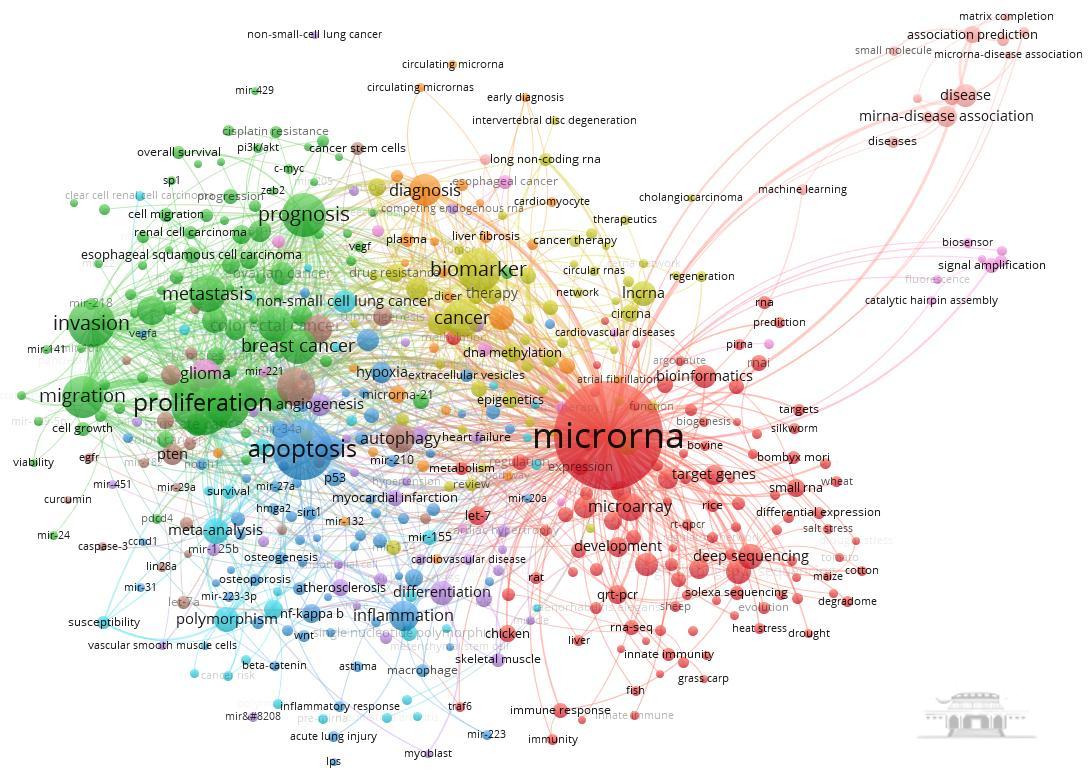
图6 2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖中国作者参与的相关施引文献关键词共现
3、 相关主题高影响力论文
Victor Ambros和Gary Ruvkun的99篇诺奖相关主题文献中被引频次较高的列举如下(按照2024年10月22日检索的被引频次降序排列),供参考。
1.Lee R C, Feinbaum R L, Ambros V.The c-elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14[J]. Cell. 1993, 75(5): 843-854. 被引频次:9485
2. Ambros V.The functions of animal microRNAs[J]. Nature. 2004, 431(7006): 350-355. 被引频次:9190
3. Reinhart B J, Slack F J, Basson M, et al.The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Nature. 2000, 403(6772): 901-906. 被引频次:3423
4. Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G.Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern-formation in c-elegans[J]. Cell. 1993, 75(5): 855-862. 被引频次:3088
5. Lee R C, Ambros V.An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Science. 2001, 294(5543): 862-864. 被引频次:2238
6. Pasquinelli A E, Reinhart B J, Slack F, et al.Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA[J]. Nature. 2000, 408(6808): 86-89. 被引频次:1817
4、 高影响力施引文献
中国作者参与的施引文献中近三年有高被引论文15篇(ESI更新时间:2024年9月)。
1. Cui Y Z, Qi Y, Ding L, et al.miRNA dosage control in development and human disease[J]. Trends In Cell Biology. 2024, 34(1): 31-47.
2. Pordel S, Khorrami M, Saadatpour F, et al.The role of microRNA-185 in the pathogenesis of human diseases: A focus on cancer[J]. Pathology Research And Practice. 2023, 249(2023-09-29)[2024-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2023.154729.
3. Kim T, Croce C M.MicroRNA: trends in clinical trials of cancer diagnosis and therapy strategies[J]. Experimental And Molecular Medicine. 2023, 55(7): 1314-1321.
4. Li S G, Zhang H Y, Zhu M, et al.Electrochemical Biosensors for Whole Blood Analysis: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives[J]. Chemical Reviews. 2023, 123(12): 7953-8039.
5. Wu Y L, Lin Z J, Li C C, et al.Epigenetic regulation in metabolic diseases: mechanisms and advances in clinical study[J]. Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy. 2023; 8(2023-03-02)[2024-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01333-7.
6. Yan C Q, Chen J, Wang C, et al.Milk exosomes-mediated miR-31-5p delivery accelerates diabetic wound healing through promoting angiogenesis[J]. Drug Delivery. 2022, 29(1): 214-228.
7. Li S H, Liu Y H, Zhang T, et al.A Tetrahedral Framework DNA-Based Bioswitchable miRNA Inhibitor Delivery System: Application to Skin Anti-Aging[J]. Advanced Materials. 2022, 34(2022-11-17) [2024-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202204287.
8. Yu F, Lee P, Yang L L, et al.The impact of sensory neuropathy and inflammation on epithelial wound healing in diabetic corneas[J]. Progress In Retinal And Eye Research. 2022, 89(2022-07) [2024-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101039.
9. Yin L F, Yan L, Yu Q, et al.Characterization of the MicroRNA Profile of Ginger Exosome-like Nanoparticles and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Intestinal Caco-2 Cells[J]. Journal Of Agricultural And Food Chemistry. 2022, 70(15): 4725-4734.
10. Chen B Q, Dragomir M P, Yang C, et al. Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy resistance[J]. SIGNAL Transduction And Targeted Therapy. 2022, 7(2022-04-13) [2024-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-00975-3.
11. Liu W, Lin H, Huang L, et al.Identification of miRNA-disease associations via deep forest ensemble learning based on autoencoder[J]. Briefings In Bioinformatics. 2022, 23(2022-05-13) [2024-10-22].https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbac104.
12. Fan C Q, Li Y, Lan T, et al.Microglia secrete miR-146a-5p-containing exosomes to regulate neurogenesis in depression[J]. Molecular Therapy. 2022, 30(3): 1300-1314.
13. Dong Q K, Hu B B, Zhang C.microRNAs and Their Roles in Plant Development[J]. Frontiers In Plant Science. 2022, 13(2022-02-18) [2024-10-22]..https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.824240.
14. Liu Y, Zeng Y, Si H B, et al.Exosomes Derived From Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Overexpressing miR-140-5p Alleviate Knee Osteoarthritis Through Downregulation of VEGFA in a Rat Model[J]. American Journal Of Sports Medicine. 2022, 50(4): 1088-1105.
15. Yu Y Y, Gui Y, Li Z J, et al.Induced Systemic Resistance for Improving Plant Immunity by Beneficial Microbes[J]. Plants-Basel. 2022, 11(2022-01-30) [2024-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030386.
纰误之处,敬请批评指正!同时,我们面向全校师生征集关注的领域和专题,欢迎提出宝贵建议。联系方式:68754550,Email:jflai@lib.whu.edu.cn。
(编辑:张惠荣 审核:刘颖、邵敏)